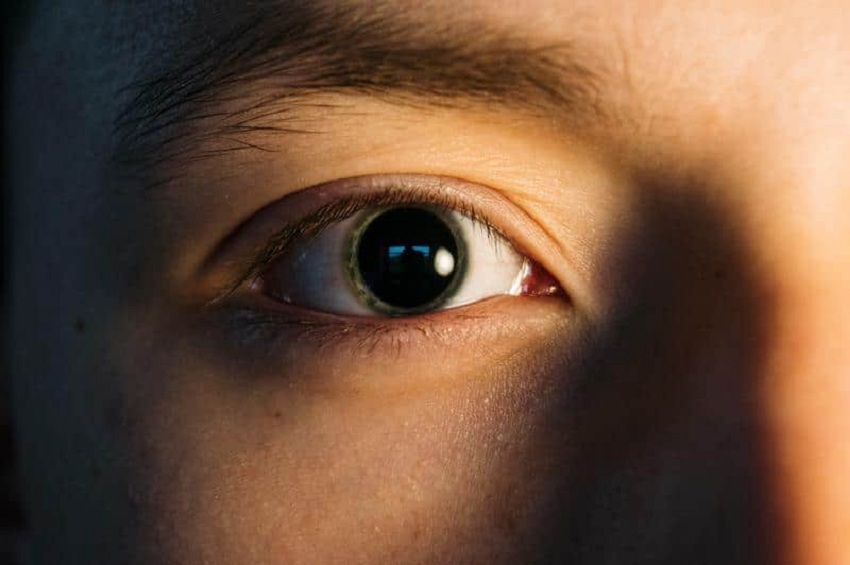
When assessing brain health and function, the eyes can reveal a lot more than you might think. A major part of this type of analysis is pupillary size measurement and how pupils respond to light and other stimuli. The reaction in a pupil can give a great deal of information about the status of the nervous system. One such measure of this response is the percent change in pupil size, an essential tool during a neuro exam. But why is that particular measure so important in neurological assessments, and how does that affect clinical decisions? Let’s dive in further.
Percent Change in Pupil Size: A Peephole into the Brain
What is the percent change in pupil size, and why does it matter? This measures the change in pupil diameter when it moves from its resting size to its constrained or dilated size when exposed to light. For example, a patient whose pupils dilate from 3 mm in low light to 6 mm: Percent change quantifies this change, giving the clinician an exact pupillary size measurement to evaluate.
This value will allow a clinician to follow the reaction over time or compare it against established baselines. Where the patient’s state may evolve rapidly, such as in the case of traumatic brain injury, these changes become increasingly important to follow. Significant descent or deviation in percent change in pupil size may indicate poor conditions and necessitate interventions promptly.
Role of Neurological Tools in Measuring Pupil Reactivity
Modern neuroscience tools like automated pupillometers make it easy for healthcare providers to obtain measurements of pupil reactivity and percent change in pupil size. Variability in pupil response that cannot be measured manually is detectable with these devices. These tools provide standardized, objective data to help control human error.
NP is one such measure by these devices. NPi combines data on percent change in pupil size, speed of reaction, and other parameters into an overall score reflecting the true neurological health. If the close approximation is found to the normal range, then it denotes that pathways from the brain that control pupil reactions are adequate. Abnormal deviations can be suggestive of problem areas that may need further examination.
Percent Change in Pupil Size Real-World Applications
Percent change in pupil size is also commonly seen in clinical settings for a patient being monitored in critical care, especially with head injuries or following surgeries that may compromise the brain. For instance, if there is a patient who has had a head trauma, one would monitor continuously the measurement of the pupillary size. A crucial sign showing pupils whose reactivity is decreased or by some enormous percentage difference away from their established percent change may be pointing towards high intracranial pressure or other developments.
This also offers continuous monitoring, even for complex conditions, through the application of neurological tools that automatically compute these changes. This allows a rapid and data-driven decision by healthcare teams with the difference of probably saving lives between knowing that a patient’s condition is worsening.
Beyond the Clinic: Understanding the Patient Perspective
Knowing the significance of pupil reactivity allows patients and families to realize how neuro exam, in general, are an important procedure. Terms like percent change in pupil size and NPi may seem like technical mumbo-jumbo, but they sum up to one central idea: the monitoring of the way the brain and the body converse with each other. A patient’s eyes are examined not only to check vision but she gets a glimpse of the status of the brain.
Families of patients with traumatic brain injuries or neurological conditions often seek signs of improvement or decline. It is sometimes helpful for families to understand that pupil measurement is a key part of this evaluation, which can clarify and reassure them about their loved one’s care.
Conclusion
The percent change in pupil size may not be the most important detail but still holds a heavy weight in neurological assessment. Using modern, sophisticated tools within the neurological line of treatment, such as automated pupillometers and the NPi, and so on, healthcare providers can make more accurate decisions and ensure better outcomes for patients. Next time you hear a doctor mention pupil reactions you will know that he’s not checking people’s vision; instead, he is uncovering a vital piece of information about the brain’s health.